Honda Civic: Fuse Box Diagrams
From the moonroof to the daytime running lights, this guide breaks down the fuse box components to help you quickly find that faulty fuse.
This article applies to the Honda Civic (1992-2000).
Fuses, located in-between the battery, are the electrical components your car draws power from. It's important to know where the fuses are located and what each fuse does, so that if you ever have a problem you know where to start looking. Always start the diagnosis of an electrical problem with its fuse because they are easy to test and pretty cheap to replace.
Honda Civic (1992-1995) Component Breakdown
Interior Fuse Box
The interior fuse box is located underneath the dashboard on the driver's side. The lid is clipped in. To remove it, swing the lid down and pull it out.
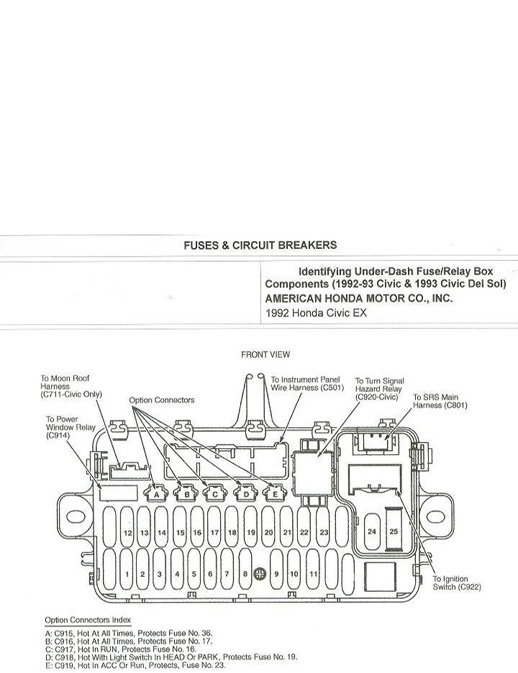
Figure 1a. Interior fuse panel diagram.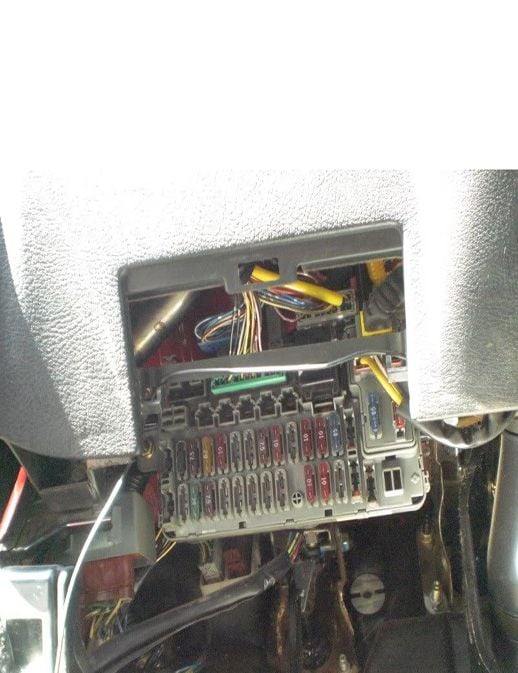 
Figure 1b. Driver's side fuse box. 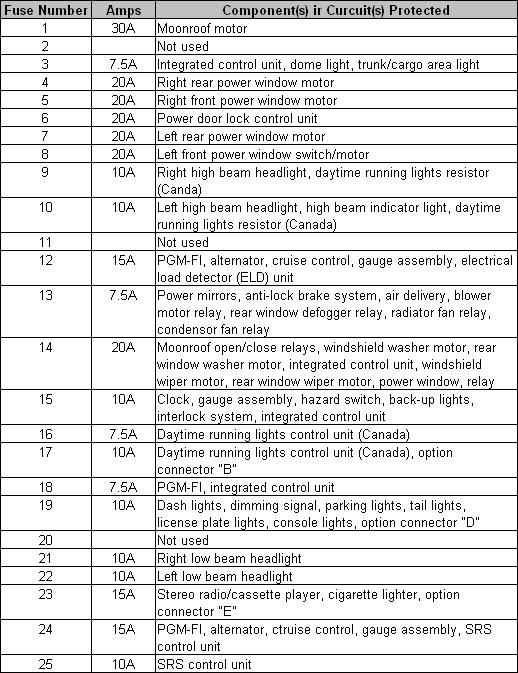
Figure 1c. Interior fuse number and circuit chart.
The interior fuse panel (Figure 1a) is located under the dash (Figure 1b). The table in Figure 1c contains the fuse, the rating, and what the fuse does. For example, if your radio stopped working, you'd need to test fuse number 23 and replace it with a new 15 amp fuse if found to be faulty. Because interior fuses commonly fail, it is recommended to keep a pack with an assortment of different amperage in the glove compartment.
Under the Hood Fuse Box
The fuse box under the hood is located next to the battery in the engine compartment.
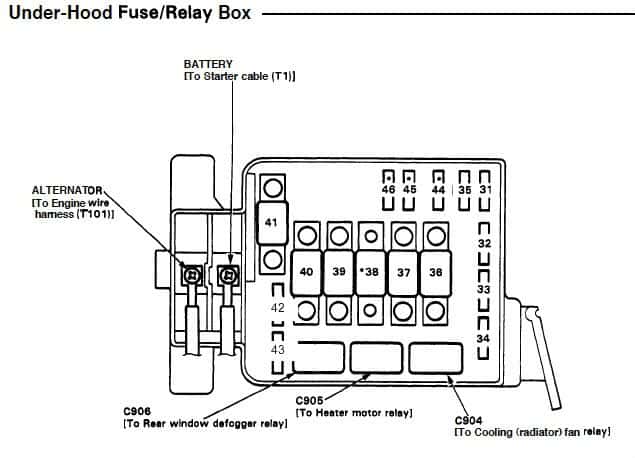
Figure 2a. Diagram of the fuse box under the hood.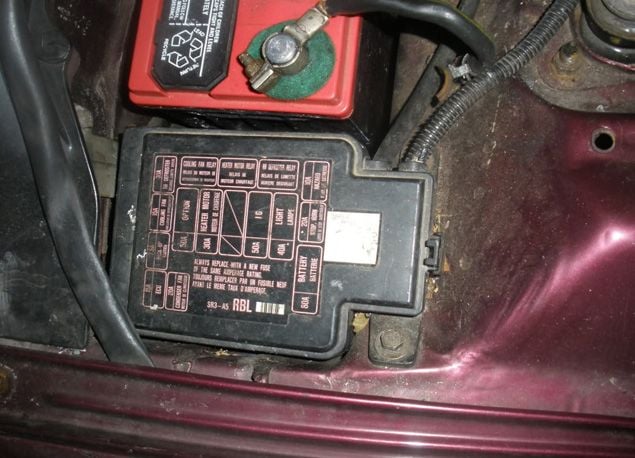 
Figure 2b. Fuse box location. 
Figure 2c. Fuse box explanation.
The diagram in Figure 2a is the layout of the fuse box located under the hood. Figure 2c gives the amperage and what the fuse—in that location—controls. These fuses are less likely to blow than the ones inside the car. That said, it'll also be less likely that there'll be a spare handily available in the event that one does. If one of these fuses does blow, it's usually a sign that there is something else wrong that caused it to fail in the first place.
Honda Civic (1996-2000) Component Breakdown
Interior Fuse Box
Figure 3a is the layout of the interior fuse panel (located under the dash), while Figure 3b is a table containing the fuse number, the rating, and what that fuse does. If the radio stopped working, for example, the next step would be to test fuse number 23 and replace it with a new 15 amp fuse if it's faulty. Interior fuses fail more frequently than under the hood fuses, which is why it is recommend keeping an assortment pack with different amperage fuses in the glove compartment.
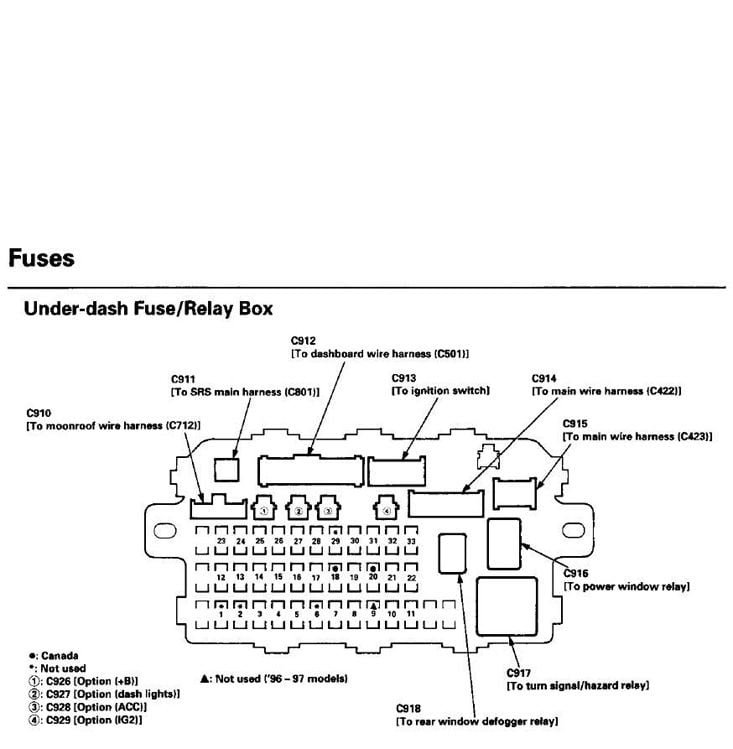
Figure 3a. Interior fuse panel diagram. 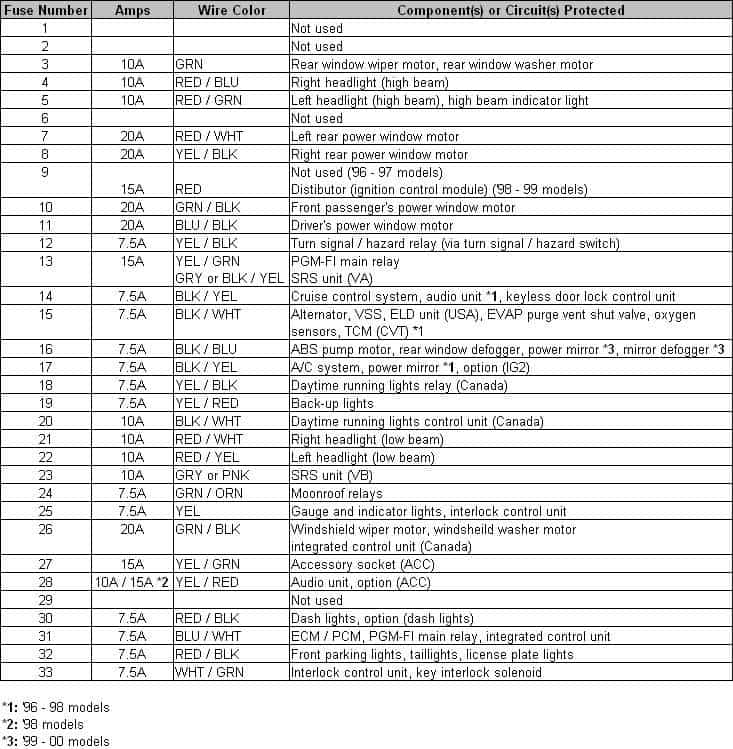
Figure 3b. Interior fuse number and circuit chart.
Under the Hood Fuse Box
Figure 4a is the layout of the fuse panel, which is located under the hood, while Figure 4b gives the amperage and what that fuse—in that location—controls. These fuses are less likely to blow and are larger fuses than ones inside the car, so it's less likely you will have a spare in the even one does. In addition, if one of these fuses does blow it's usually a sign that there is something else wrong that caused it to fail in the first place.
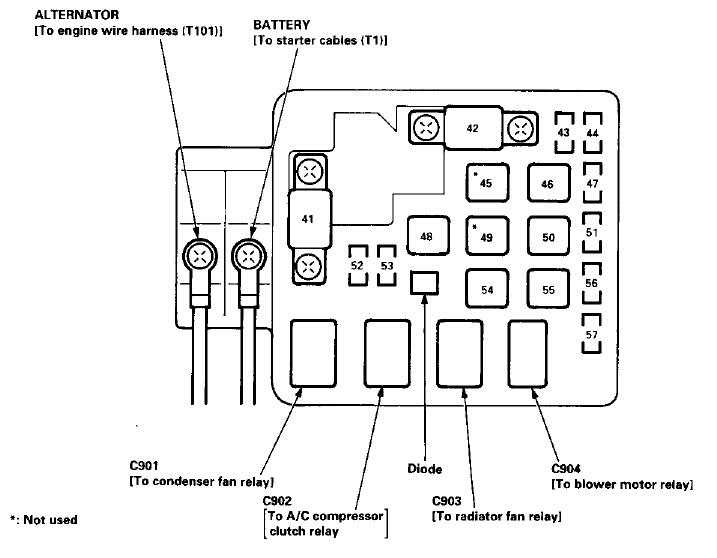
Figure 4a. Fuse box located under the hood diagram. 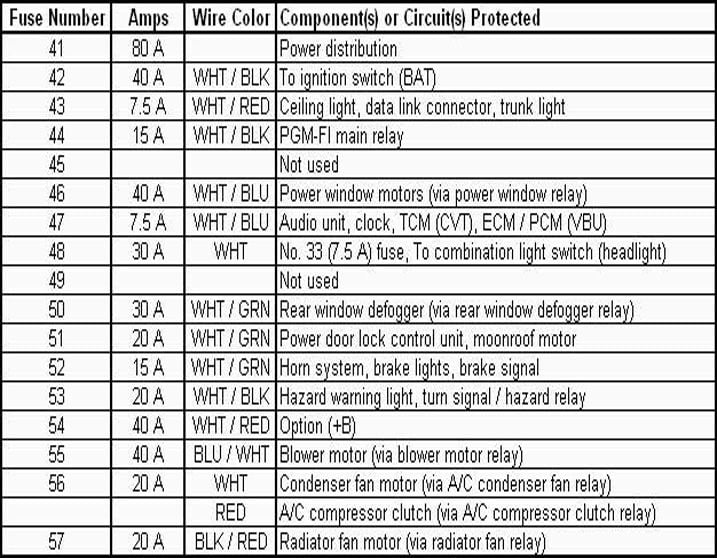
Figure 4b. Under the hood fuse box explanation.
Common Questions
What Do Fuses Do?
The purpose of a fuse is to protect components from a current overload. Overloading electronics can easily lead to electrical fire. The amperage rating on the fuse is matched to the maximum amount needed of whatever it controls, and the gauge of the wire running from the battery to the fuse of that item. This is why replacing a fuse with the correct amperage is critical.
What Causes Fuses to Blow?
The two main reasons fuses blow are increased electrical resistance or a shorted wire. Excessive resistance is usually caused by corrosion on the fuse legs, which can come with age and the environment. A wire can short for any any number of reasons, but generally it's caused by a wire rubbing against a metal surface. Dry rot in the wiring's rubber casing can cause it to eventually break away, which exposes a bare wire.
How Can I Check if a Fuse is Blown?
Fuse testers are available for a few dollars at the local auto part store. These testers simulate a simple circuit and will tell you whether or not a fuse has blown. Another option is to use a multimeter as described in Figures 5a and 5b below. A multimeter is a device that measures electrical signals with two prongs (one positive, one negative). You would stock the prongs into the fuse and measure the amperage (amps) coming from one side to the other. Fuses are marked by their amerage, hence the "10" on Figure 5c.

Figure 5a. How to test a fuse. 
Figure 5b. How to test a fuse. 
Figure 5c. Multimeters are an inexpensive security when dealing with fuses.
Related Discussions and Site
- Honda Civic Service Manual (1996 to 2000) - ManualsLib.com
- Honda Civic/Del Sol Fuse Diagrams - Honda-Tech.com
- Honda Civic/Del Sol How to Test Fuses - Honda-Tech.com






